.
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognoses, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting health.
Medicine encompasses a variety of healthcare practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness and malfunction.
Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetic, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injuries and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.
Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time, it was an art (an area of creativity and skill), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local cultures, for example, a medicine man would apply herbs and also says prayers for healing, or an ancient philosopher and physician would apply bloodletting according to the theories of humorism.
In recent centuries, since the advent of modern science, most medicine has become a combination of art and science (both basic and applied, under the umbrella of medical science); for example, switching techniques for sutures is an art learned through practice, the knowledge of, what happens at the cellular and molecular level in the tissues, being stitched, arises through science. Pre-scientific forms of medicine, now known as traditional medicine or folk medicine, remain commonly, in use, in the absence of scientific treatment and are thus called alternative medicine
![]()
List of all the medicine have been practiced throughout human history
It is not possible to list all the medicines that have been practiced throughout human history as the history of medicine spans thousands of years and involves a vast array of cultures, regions, and practices. Additionally, many of these practices may no longer be in use or have been replaced by modern medicine. However, some notable historical medical practices include Traditional Chinese Medicine, Ayurveda, Greek medicine, Egyptian medicine, and Native American medicine, among others. It is important to note that not all historical medical practices were safe or effective, and some may have even been harmful.

1- Traditional Chinese Medicine: This system of medicine has been practiced in China for thousands of years and involves the use of various herbs, acupuncture, massage, and other therapies to treat a wide range of conditions.
2- Ayurveda: This traditional Indian system of medicine is based on the concept of balancing the body, mind, and spirit through the use of herbs, diet, and lifestyle practices.
3- Greek Medicine: The ancient Greeks made significant contributions to the field of medicine, including the development of the Hippocratic Oath and the concept of the four humors, which held that illness was caused by imbalances in bodily fluids.
4- Egyptian Medicine: Ancient Egyptian medicine was based on a combination of practical knowledge and magical beliefs. It involved the use of herbs, surgery, and other therapies.
5- Native American Medicine: Many indigenous peoples in North America have their own traditional healing practices, which involve the use of herbs, rituals, and other therapies.
6–Mesopotamia Medicine:
It’s important to note that while these practices have been widely used throughout history, not all of them have been proven to be safe or effective, and some may even be harmful.

![]()
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
TCM is a system of healing that has been practiced for thousands of years in China. TCM incorporates a range of practices, including acupuncture, herbal medicine, dietary therapy, and massage. It is based on the principles of balancing the body’s energy, or qi (pronounced “chee”), to maintain health and prevent disease.
Acupuncture: In acupuncture, thin needles are inserted into specific points on the body to stimulate the flow of qi. These points are located along channels, or meridians, that run throughout the body. Acupuncture is used to treat a range of conditions, including pain, digestive issues, and anxiety.
Herbal medicine: TCM uses a range of herbal remedies to treat illnesses and promote health. Herbs are prescribed based on the individual’s specific symptoms and constitution. Herbs can be taken in a variety of forms, including teas, powders, and capsules.
Dietary therapy: In TCM, food is considered a powerful form of medicine. Dietary therapy involves making dietary changes to promote health and treat illnesses. Foods are classified as hot or cold, and yin or yang, and are used to balance the body’s energy.
Massage: TCM includes a range of massage techniques, including acupressure and tui na. These techniques are used to stimulate the flow of qi and promote relaxation and healing.
Cupping: Cupping involves placing cups on the skin to create a vacuum, which stimulates blood flow and promotes healing. Cupping is often used to treat pain, respiratory issues, and digestive problems.
Moxibustion: Moxibustion involves burning an herb called mugwort to warm and stimulate specific points on the body. Moxibustion is used to treat a range of conditions, including pain, digestive issues, and menstrual problems.
TCM is based on the idea that the body is a complex system that is interconnected and constantly in flux. By addressing imbalances in the body’s energy, TCM aims to promote health and prevent disease.
Ayurvedic Medicine:
Detailed Description:
Ayurvedic medicine is a traditional healing system that originated in India over 5,000 years ago. It is based on the belief that health and wellness depend on a delicate balance between the mind, body, and spirit.
Ayurvedic medicine uses a holistic approach to health, taking into account all aspects of a person’s life, including diet, lifestyle, emotions, and environment. The primary goal of Ayurvedic medicine is to promote good health rather than simply treating illness.
Ayurvedic medicine is based on the concept of the three doshas: vata, pitta, and kapha. These doshas represent different elements and are believed to be present in varying degrees in every person. Each dosha has its own set of physical and emotional characteristics, and imbalances can lead to illness.

Ayurvedic practitioners use a variety of treatments to restore balance and promote good health, including dietary changes, herbal remedies, massage, yoga, meditation, and detoxification. Ayurvedic massage, known as Abhyanga, involves the use of warm oil and gentle pressure to promote relaxation and balance.
Herbal remedies are a cornerstone of Ayurvedic medicine. Many plants and herbs are believed to have healing properties, and Ayurvedic practitioners use a variety of formulas and preparations to address specific health concerns.
One of the unique aspects of Ayurvedic medicine is its emphasis on individualized treatment. Ayurvedic practitioners take into account a person’s unique physical and emotional makeup, as well as their environment and lifestyle, to develop a customized treatment plan.
While Ayurvedic medicine has gained popularity in the West in recent years, it has also faced criticism for its lack of scientific evidence and potential health risks associated with certain treatments. It is important to work with a qualified practitioner and to discuss any potential risks or side effects before starting Ayurvedic treatment

**Greek Medicine: **detailed descriptions Greek medicine refers to the healing practices and theories of the ancient Greeks, which had a significant influence on the development of Western medicine.
The earliest Greek medical texts date back to the 5th century BCE, with the most famous being the Hippocratic Corpus, a collection of works attributed to the physician Hippocrates. Hippocrates is known as the “father of medicine” and is credited with the development of the Hippocratic Oath, which is still taken by modern physicians.
One of the key principles of Greek medicine was the belief in the four humors: blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile. According to this theory, good health was achieved when these humors were in balance, and illness occurred when there was an imbalance. Greek physicians used a variety of treatments to restore this balance, including dietary changes, exercise, and medicinal herbs.
Greek medicine also emphasized the importance of observation and clinical diagnosis. Physicians were encouraged to carefully observe their patients and record their symptoms and treatment outcomes. This focus on empirical observation was a major departure from earlier medical traditions, which relied on magical and religious beliefs.
Surgery was also an important aspect of Greek medicine. Greek physicians were skilled in a variety of surgical techniques, including amputations, trepanation, and cataract removal. They also developed a rudimentary understanding of anatomy and physiology, based on observations of animal dissections.
Overall, Greek medicine was a significant precursor to modern Western medicine, with many of its principles and practices continuing to influence medical practice today. Its emphasis on observation, clinical diagnosis, and surgical techniques laid the foundation for the scientific approach to medicine that developed in the centuries that followed.

Ancient Egyptian medicine was a complex system that developed over thousands of years. It was based on a combination of empirical observation, magical and religious beliefs, and a rudimentary understanding of anatomy and physiology.
Egyptian physicians were highly respected members of society and were often trained in temple schools. They used a variety of treatments including medicinal herbs, surgeries, and magical spells. Medical texts, such as the Ebers Papyrus and the Edwin Smith Papyrus, provide detailed instructions on the diagnosis and treatment of various ailments.
Some of the most common ailments treated by Egyptian physicians included wounds, infections, dental problems, and digestive issues. They also had a rudimentary understanding of the circulatory system, as evidenced by the mummification process.
One of the most interesting aspects of ancient Egyptian medicine was the emphasis on preventative care. Physicians encouraged healthy lifestyles, including regular exercise and a balanced diet. They also believed that maintaining a positive attitude and avoiding negative emotions was important for overall health.
While ancient Egyptian medicine may seem primitive by modern standards, it was an important precursor to modern medicine. Many of the treatments and techniques developed by the Egyptians were passed down to later civilizations and have influenced modern medical practices

Native American Medicine:
detailed descriptions Native American medicine is a broad term that refers to the traditional healing practices of Indigenous peoples in North America. These practices vary among different tribes and nations, but they share some common principles.
One of the key principles of Native American medicine is the belief that all things in nature are interconnected, and that the physical, emotional, and spiritual aspects of a person must be in balance for good health. Native healers, also known as medicine people, use a variety of techniques to restore this balance.
Herbal remedies are a common form of Native American medicine. Many plants, such as sage, cedar, and sweetgrass, are believed to have healing properties and are used for various purposes. For example, sage is often burned in smudging ceremonies to purify the air and promote spiritual balance.
Ceremonies and rituals are also an important part of Native American healing practices. Sweat lodges, vision quests, and pipe ceremonies are examples of rituals that are used to promote physical and spiritual healing. These ceremonies often involve the use of music, prayer, and meditation to help individuals connect with the spirit world.
Storytelling is another important aspect of Native American medicine. Traditional stories and myths are used to convey important cultural values and teach individuals about their place in the world. These stories can also be used as a form of therapy, helping individuals to work through emotional and psychological issues.
Overall, Native American medicine emphasizes the interconnectedness of all things and the importance of maintaining balance in all aspects of life. While these practices have been marginalized and suppressed by colonialism and modern medicine, they continue to play an important role in the healing and well-being of many Indigenous communities.

Mesopotamia medicine:
Mesopotamia, a region that roughly corresponds to modern-day Iraq, was home to several ancient civilizations such as the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. These civilizations had their own unique medical practices, which were often intertwined with religion and magic.
One of the earliest recorded medical texts is the “Diagnostic Handbook,” which was written in Sumeria around 2500 BCE. This text includes descriptions of various illnesses and their treatments, including the use of medicinal herbs and other remedies. The ancient Babylonians and Assyrians also developed their own medical practices, which involved the use of herbs, massage, and surgery.
One of the most famous Mesopotamian medical texts is the “Assyrian Herbal,” which was written in the 7th century BCE and contains descriptions of over 250 plants and their medicinal uses. The text also includes recipes for various remedies, such as ointments and poultices.
![]()
Mesopotamia Medicine detailed descriptions
Mesopotamia, the region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in present-day Iraq, was home to some of the earliest civilizations in human history, including the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. Medicine in Mesopotamia was closely tied to religion and magic, and many medical practices were performed by priests or sorcerers.
Some of the key features of Mesopotamian medicine include:
1- The use of magical and religious rituals: Many illnesses were thought to be caused by evil spirits, and healing often involved rituals that were intended to drive out these spirits. These rituals could include incantations, sacrifices, and the use of amulets.
2- The use of herbal remedies: Mesopotamian healers were familiar with a wide range of plants and their medicinal properties. They used these plants to create poultices, teas, and other remedies to treat a variety of ailments.
3 – The practice of surgery: Mesopotamian surgeons were skilled in performing procedures like trepanation (drilling a hole in the skull) and castration (removing the testicles). These procedures were often performed without anesthesia, and the survival rate was low.
4- The use of diagnostic techniques: Mesopotamian healers used a variety of techniques to diagnose illness, including examining the patient’s urine, observing the color and texture of their skin, and feeling their pulse.
5- The development of medical texts: Mesopotamian healers recorded their knowledge in written texts, some of which have survived to this day. These texts include the “Diagnostic Handbook,” a guide to diagnosing various illnesses, and the “Medical Encyclopedia,” a comprehensive guide to Mesopotamian medicine.
Overall, Mesopotamian medicine was a complex and multifaceted system that drew on a wide range of knowledge and practices. While some of its practices may seem primitive by modern standards, it was an important precursor to modern medicine and helped pave the way for many of the medical advances that we enjoy today
03:08
How many types of medicines are in practice other than Allopathy?
There are several types of medicines in practice other than allopathy, including but not limited to:
1- Ayurvedic medicine
2- Homeopathic medicine
3- Traditional Chinese medicine
4- Naturopathic medicine
5- Unani medicine
6- Siddha medicine
7 – Acupuncture
8- Chiropractic
9- Herbal medicine
10- Naturopathy
11- Osteopathy
12- Alternative medicine
13- Complementary medicine
14- Integrative medicine
15- Functional medicine
16- Palliative medicine
17- Sports medicine
18- Occupational medicine
19- Preventive medicine
20- Rehabilitation medicine
21- Longevity Medicine
It’s important to note that the efficacy and safety of these alternative forms of medicine vary and some may not have scientific evidence to support their use. It’s always recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before trying any new form of medicine.
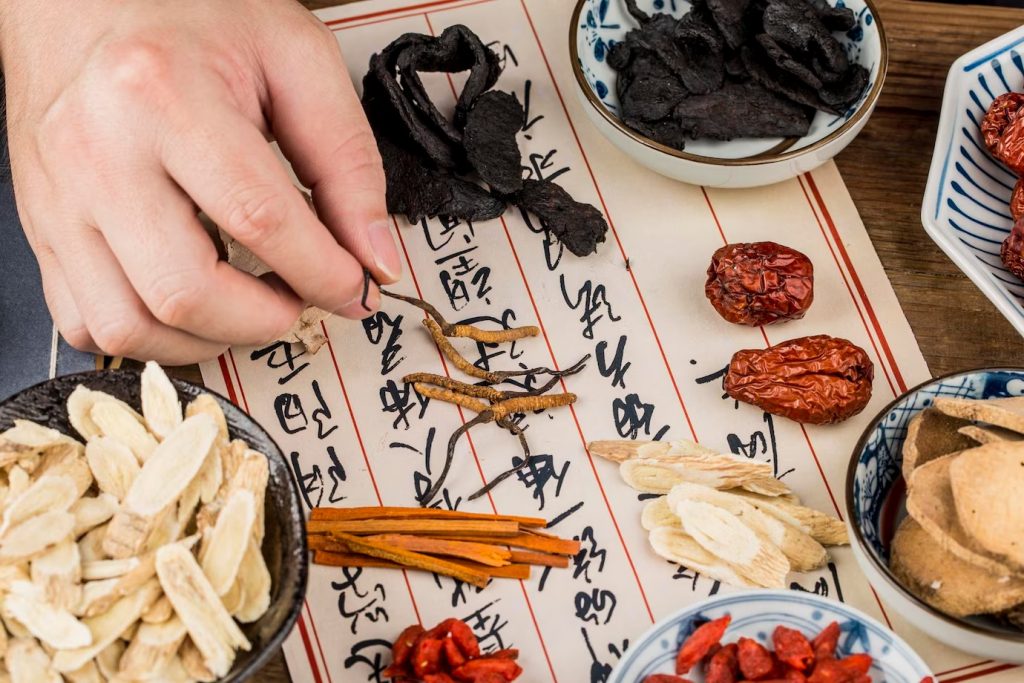

![]()
Chinese Medicine
Chinese medicine and indigenous medicine and Chinese medicine and indigenous medicine are two types of traditional medicine.
Chinese medicine is a holistic system of medicine that originated in China and has been practiced for thousands of years. It includes practices such as acupuncture, herbal medicine, dietary therapy, and exercises like tai chi and qigong. Chinese medicine is based on the concept of Qi (pronounced “chee”), which is the vital energy that flows through the body’s meridian pathways, and the balance of Yin and Yang energies. The goal of Chinese medicine is to restore balance and harmony to the body, mind, and spirit.
Indigenous medicine, also known as traditional medicine, is a type of medicine that has been developed and practiced by various indigenous communities around the world. It includes practices such as the use of plants and herbs, spiritual healing, and physical therapies like massage and acupuncture. Indigenous medicine is often closely tied to the culture, spirituality, and traditions of the community that practices it.
It’s important to note that while traditional medicines have been used for centuries and may have cultural significance, the safety and efficacy of these practices may not have been scientifically validated, and it’s always recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before trying any new form of medicine.
No events today
06:44
Open sidebar
Ayurvedic Medicine Overview.
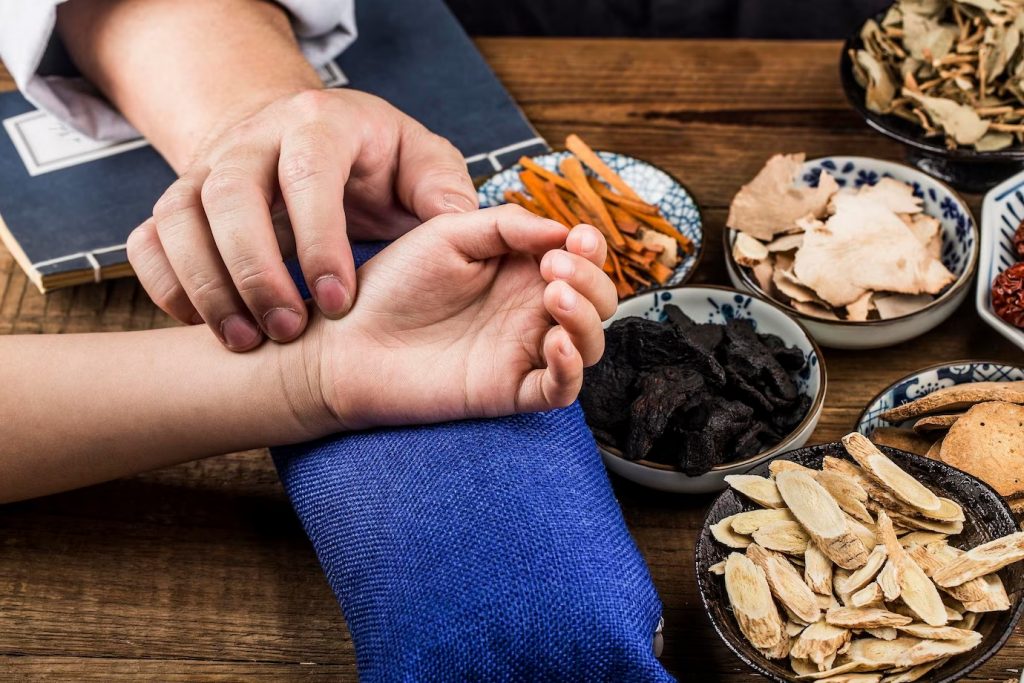

![]()
Ayurvedic medicine Detailed description
Ayurvedic medicine is a traditional healing system that originated in India over 5,000 years ago. It is based on the belief that health and wellness depend on a delicate balance between the mind, body, and spirit. The goal of Ayurveda is to promote good health, prevent illness, and treat disease by restoring balance within the body.
Ayurvedic medicine uses a holistic approach that includes herbal remedies, dietary recommendations, lifestyle changes, yoga, and meditation to promote physical, mental, and spiritual health. The three main elements or doshas that Ayurvedic medicine focuses on are Vata, Pitta, and Kapha, which represent different qualities or energies in the body.
Ayurvedic practitioners diagnose imbalances in the doshas through pulse diagnosis, tongue examination, and other methods, and then develop a personalized treatment plan to restore balance. Ayurvedic remedies can include herbal supplements, massage, detoxification treatments, and dietary changes.
While Ayurvedic medicine has gained popularity in many parts of the world, it is important to note that it is not a substitute for conventional medicine and should be used as a complementary approach to healthcare. It is also important to seek the guidance of a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner to ensure safe and effective treatment.

![]()
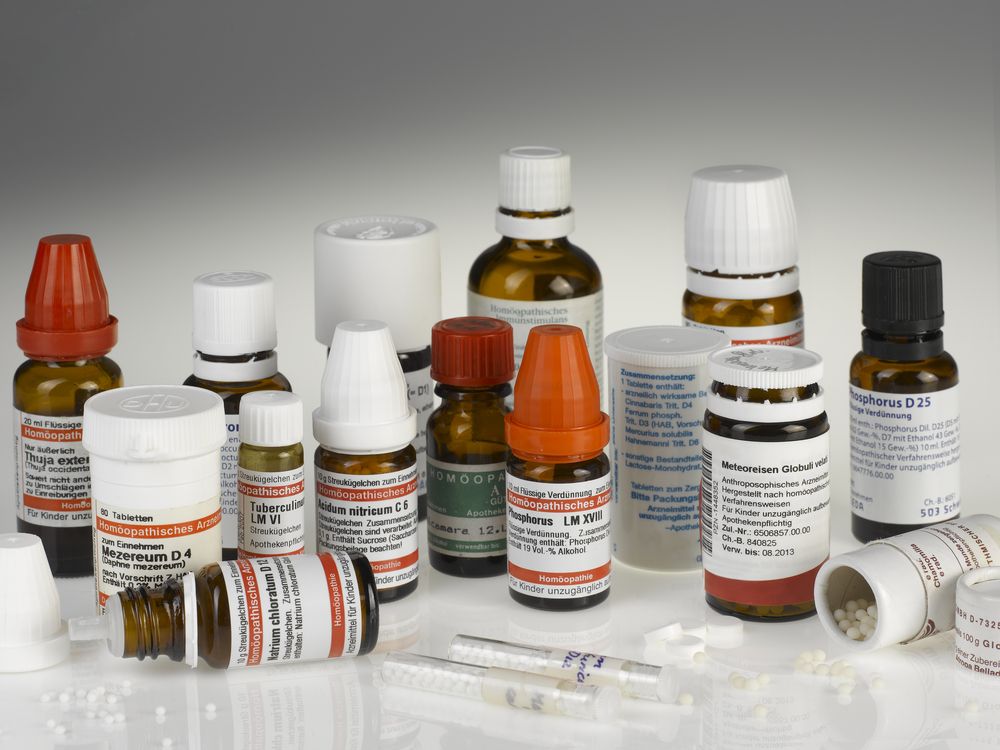
Homeopathic medicine Detailed description
Homeopathy is a system of alternative medicine that was developed in the late 18th century by German physician Samuel Hahnemann. It is based on the principle of “like cures like”, which means that a substance that causes symptoms in a healthy person can be used in diluted form to treat similar symptoms in a sick person.
Homeopathic remedies are prepared using a process called potentization, which involves diluting a substance in water or alcohol and then shaking it vigorously. The more dilute the remedy, the more potent it is believed to be. Homeopathic remedies are available in various forms, including tablets, liquids, creams, and gels.
The selection of a homeopathic remedy is based on the individual’s unique symptoms, personality, and medical history. Homeopathic practitioners use a holistic approach to diagnose and treat the whole person, not just the specific illness or symptom.
Homeopathy is used to treat a wide range of conditions, including allergies, asthma, arthritis, anxiety, depression, digestive disorders, and skin conditions. However, the effectiveness of homeopathic remedies has been a subject of debate, as many studies have shown mixed results.
It is important to note that homeopathy should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatment in the case of serious or life-threatening illnesses. Homeopathic remedies are generally considered safe, but they can cause side effects or interact with other medications. It is recommended to consult a qualified homeopathic practitioner before using homeopathic remedies.

![]()
Traditional Chinese medicine Detailed descriptions
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is a system of healing that has been used in China for thousands of years. It is based on the concept of Qi (pronounced “chee”), which is the vital energy that flows through the body’s meridians, or energy channels.
TCM uses a holistic approach to diagnose and treat illness, focusing on the balance and harmony of the body, mind, and spirit. The TCM system includes acupuncture, herbal medicine, dietary therapy, massage, and exercise, such as Tai Chi and Qigong.
Acupuncture is a key component of TCM and involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points on the body to balance the flow of Qi and restore health. Herbal medicine is also widely used in TCM and involves the use of natural substances, such as plants, minerals, and animal products, to promote healing and prevent illness.
TCM also emphasizes the importance of nutrition and dietary therapy, with recommendations tailored to each individual’s unique constitution and condition. Massage and bodywork are used to promote circulation and relieve tension, while exercises such as Tai Chi and Qigong are used to balance Qi and promote overall wellness.
TCM is used to treat a wide range of conditions, including pain, digestive disorders, respiratory problems, gynecological issues, emotional disorders, and neurological conditions. While TCM has gained popularity in many parts of the world, it is important to note that it is not a substitute for conventional medical treatment and should be used as a complementary approach to healthcare.
It is recommended to seek the guidance of a qualified TCM practitioner to ensure safe and effective treatment. TCM practitioners use a personalized approach to diagnose and treat each patient, based on their unique symptoms and individual constitution.

![]()
Naturopathic medicine Detailed descriptions
Naturopathic medicine is a system of healthcare that focuses on the body’s natural ability to heal itself. It combines traditional healing methods with modern medical knowledge to promote wellness and prevent disease.
Naturopathic doctors (NDs) use a holistic approach to diagnose and treat illness, taking into account the patient’s physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual health. They use a variety of natural therapies, including herbal medicine, nutritional therapy, homeopathy, acupuncture, and lifestyle counseling.
Herbal medicine is a key component of naturopathic medicine, with NDs using plants and natural substances to promote healing and prevent illness. Nutritional therapy involves the use of diet and supplements to promote optimal health and treat a wide range of conditions. Homeopathy uses highly diluted substances to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes, while acupuncture involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points on the body to promote balance and relieve pain.
NDs also use lifestyle counseling to help patients make positive changes to their daily habits, such as exercise, stress reduction, and sleep. In addition, they may use laboratory testing and other diagnostic tools to assess a patient’s overall health and make appropriate treatment recommendations.
Naturopathic medicine is used to treat a wide range of conditions, including digestive disorders, allergies, hormonal imbalances, chronic pain, and mental health conditions. It is generally considered safe, but it is important to note that it should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatment in the case of serious or life-threatening illnesses.
It is recommended to seek the guidance of a qualified naturopathic doctor to ensure safe and effective treatment. NDs use a personalized approach to diagnose and treat each patient, based on their unique symptoms and individual health history.

![]()
Unani medicine Detailed descriptions
Unani medicine is a system of traditional medicine that originated in ancient Greece and was further developed in Persia and India. It is based on the principles of humoral theory, which states that the body is composed of four humors (blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile) that need to be in balance for good health.
Unani medicine uses a holistic approach to diagnose and treat illness, taking into account the patient’s physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual health. It emphasizes the importance of a healthy diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes to promote wellness and prevent disease.
Unani medicine uses a wide range of natural remedies, including herbal medicine, dietary therapy, massage, and cupping therapy. Herbal medicine is a key component of Unani medicine, with practitioners using a variety of natural substances, such as plants, minerals, and animal products, to promote healing and prevent illness. Dietary therapy involves the use of specific foods and dietary changes to promote optimal health and treat various conditions.
Massage and cupping therapy are also used to promote circulation and relieve tension. Unani medicine also uses diagnostic techniques, such as pulse diagnosis, to assess a patient’s overall health and make appropriate treatment recommendations.
Unani medicine is used to treat a wide range of conditions, including respiratory disorders, digestive disorders, skin conditions, and mental health conditions. It is generally considered safe, but it is important to note that it should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatment in the case of serious or life-threatening illnesses.
It is recommended to seek the guidance of a qualified Unani practitioner to ensure safe and effective treatment. Practitioners use a personalized approach to diagnose and treat each patient, based on their unique symptoms and individual health history.

![]()
Siddha medicine Detailed descriptions
Siddha medicine is a system of traditional medicine that originated in South India and has been practiced for thousands of years. It is based on the principles of Ayurveda, but with a distinct focus on the use of minerals and metals in medicinal preparations.
Siddha medicine uses a holistic approach to diagnose and treat illness, taking into account the patient’s physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual health. It emphasizes the importance of a healthy lifestyle, including diet, exercise, and meditation, to promote wellness and prevent disease.
Siddha medicine uses a wide range of natural remedies, including herbal medicine, mineral and metal preparations, and dietary therapy. Herbal medicine is a key component of Siddha medicine, with practitioners using a variety of natural substances, such as plants, to promote healing and prevent illness. Mineral and metal preparations, known as bhasmas, are also commonly used in Siddha medicine for their medicinal properties.
Dietary therapy involves the use of specific foods and dietary changes to promote optimal health and treat various conditions. Siddha medicine also uses diagnostic techniques, such as pulse diagnosis, to assess a patient’s overall health and make appropriate treatment recommendations.
Siddha medicine is used to treat a wide range of conditions, including respiratory disorders, digestive disorders, skin conditions, and mental health conditions. It is generally considered safe, but it is important to note that it should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatment in the case of serious or life-threatening illnesses.
It is recommended to seek the guidance of a qualified Siddha practitioner to ensure safe and effective treatment. Practitioners use a personalized approach to diagnose and treat each patient, based on their unique symptoms and individual health history.
![]()
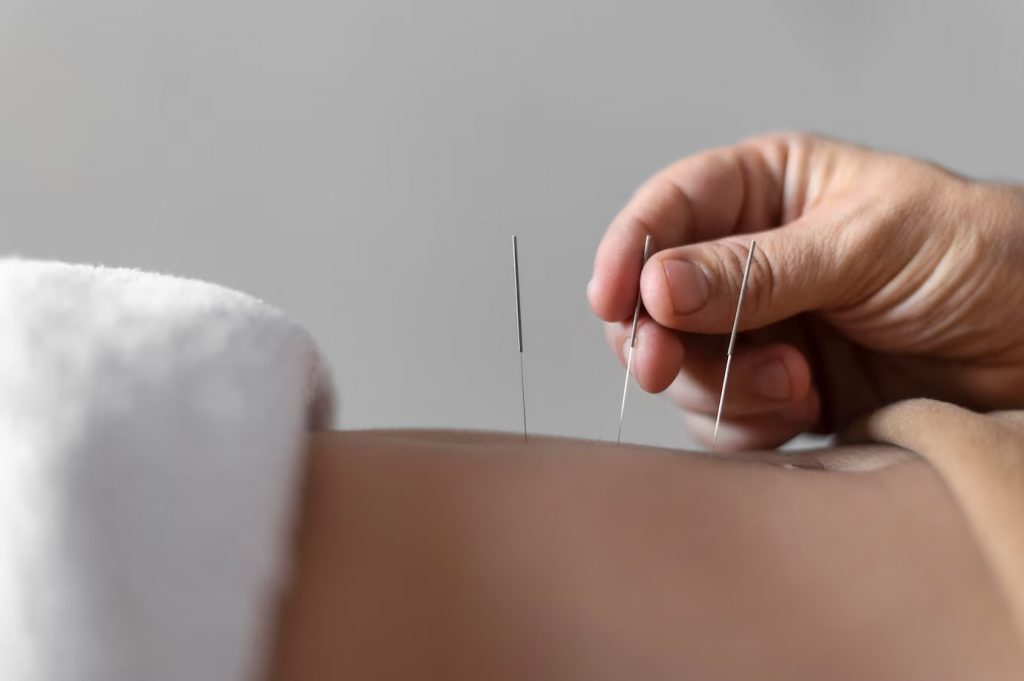
Acupuncture Detailed descriptions
Acupuncture is a form of traditional Chinese medicine that involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points on the body to promote balance and relieve pain. The practice is based on the belief that the body’s vital energy, or qi, flows along channels, or meridians, throughout the body, and that blockages or imbalances in these channels can lead to illness or pain.
During an acupuncture treatment, a practitioner will insert thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the flow of qi and restore balance. The needles are typically left in place for 10-30 minutes, and the practitioner may gently manipulate them to enhance their effects.
Acupuncture is used to treat a wide range of conditions, including chronic pain, digestive disorders, respiratory disorders, and mental health conditions. It is generally considered safe, with minimal side effects, but it is important to note that it should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatment in the case of serious or life-threatening illnesses.
In addition to needle acupuncture, other forms of acupuncture may involve the use of heat (moxibustion), pressure (acupressure), or electricity (electro-acupuncture) to stimulate the flow of qi. Some practitioners may also use cupping or gua sha, which involve the use of suction cups or scraping tools to release tension and promote circulation.
It is recommended to seek the guidance of a qualified acupuncture practitioner to ensure safe and effective treatment. Practitioners use a personalized approach to diagnose and treat each patient, based on their unique symptoms and individual health history.

![]()
Chiropractic
Detailed descriptions Chiropractic is a healthcare profession that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disorders of the musculoskeletal system and the nervous system, with an emphasis on the spine. Chiropractors use a hands-on approach to manipulate and adjust the spine and other joints to improve mobility and alleviate pain.
Chiropractic care is based on the principle that the body has an innate ability to heal itself, and that the musculoskeletal system is interconnected with other systems in the body, including the nervous system. Chiropractors aim to restore balance and alignment to the body, allowing it to function optimally and heal naturally.
Chiropractic care typically involves a physical exam, including a review of the patient’s medical history, and may also include diagnostic tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans. Based on the patient’s condition and individual needs, the chiropractor will develop a treatment plan that may include spinal adjustments, mobilization, stretching, and soft tissue therapy.
Chiropractic care is commonly used to treat a variety of musculoskeletal conditions, such as back pain, neck pain, and headaches, as well as other conditions that may affect the nervous system, such as sciatica, carpal tunnel syndrome, and fibromyalgia. Chiropractic care is generally safe and non-invasive, with few side effects, and may be used alone or in conjunction with other forms of medical treatment.
It is recommended to seek the guidance of a qualified chiropractor to ensure safe and effective treatment. Practitioners use a personalized approach to diagnose and treat each patient, based on their unique symptoms and individual health history.

![]()
Herbal medicine detailed descriptions
Herbal medicine, also known as herbalism or botanical medicine, is a system of medicine that uses plants or plant extracts to promote healing and treat illness. It is one of the oldest forms of medicine and is practiced in many cultures around the world.
Herbal medicine uses a holistic approach to diagnose and treat illness, taking into account the patient’s physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual health. Practitioners of herbal medicine use a wide range of plant-based remedies, including leaves, flowers, stems, roots, and seeds, as well as preparations made from these plant parts, such as teas, tinctures, powders, and ointments.
Herbal medicine is used to treat a wide range of conditions, including digestive disorders, respiratory conditions, skin conditions, and mental health conditions. Some herbs have been shown to have specific medicinal properties, such as anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, or antispasmodic effects.
Herbal medicine is generally considered safe, but it is important to note that not all herbs are safe for everyone, and some may interact with other medications. It is recommended to seek the guidance of a qualified herbalist or healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Herbal medicine may be used alone or in conjunction with other forms of medical treatment, and practitioners often use a personalized approach to diagnose and treat each patient, based on their unique symptoms and individual health history.

![]()
Osteopathy detailed descriptions
Osteopathy is a system of healthcare that focuses on the structure and function of the musculoskeletal system, as well as the body’s ability to heal itself. Osteopathic practitioners use a hands-on approach to diagnose and treat illness and injury, with an emphasis on the relationship between the body’s structure and its function.
Osteopathic treatment may involve a range of techniques, including joint mobilization, soft tissue massage, stretching, and manipulation. Practitioners of osteopathy may also incorporate other modalities, such as acupuncture, nutritional counseling, and exercise therapy, to promote healing and restore balance to the body.
Osteopathy is used to treat a wide range of conditions, including musculoskeletal pain, sports injuries, respiratory conditions, and digestive disorders. Osteopathic treatment is generally considered safe and non-invasive, with few side effects.
It is recommended to seek the guidance of a qualified osteopath to ensure safe and effective treatment. Osteopaths use a personalized approach to diagnose and treat each patient, based on their unique symptoms and individual health history. They may work in conjunction with other healthcare providers to provide comprehensive care and treatment.

![]()
Alternative medicine
Alternative medicine is a term that is used to describe a broad range of practices and therapies that are not typically included in mainstream, Western medicine. Alternative medicine may be used in place of, or in conjunction with, conventional medical treatment, and often focuses on a holistic approach to health and wellness.
Alternative medicine practices may include herbal medicine, acupuncture, chiropractic, osteopathy, naturopathic medicine, homeopathy, and other forms of traditional medicine, such as Ayurvedic and Traditional Chinese Medicine.
While many alternative medicine practices have been used for centuries and have been shown to have some benefits, they may not be supported by scientific evidence or may not have undergone rigorous testing to determine their safety and efficacy. It is important to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider before using any alternative medicine practices or therapies, to ensure safe and effective treatment.
It is also important to note that some alternative medicine practices may have risks or side effects, and may interact with other medications or treatments. It is recommended to approach alternative medicine with an open mind, but also with a critical eye, and to use caution and common sense when considering any form of treatment.

![]()
Complementary medicine Detailed description
Complementary medicine is a term that is used to describe a range of practices and therapies that are used in conjunction with conventional medical treatment. Complementary medicine may include practices such as acupuncture, massage therapy, herbal medicine, and other forms of traditional medicine.
Complementary medicine is often used to address the physical, emotional, and spiritual aspects of health and wellness, and may be used to alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and support the body’s natural healing processes.
Complementary medicine is often used in conjunction with conventional medical treatment, and may be recommended by healthcare providers to enhance the effectiveness of treatment or to alleviate side effects of conventional medical treatment.
While many complementary medicine practices have been shown to have some benefits, they may not be supported by scientific evidence or may not have undergone rigorous testing to determine their safety and efficacy. It is important to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider before using any complementary medicine practices or therapies, to ensure safe and effective treatment.
It is also important to note that some complementary medicine practices may have risks or side effects, and may interact with other medications or treatments. It is recommended to approach complementary medicine with an open mind, but also with a critical eye, and to use caution and common sense when considering any form of treatment.

![]()
Integrative medicine Detailed descriptions
Integrative medicine is a holistic approach to healthcare that combines conventional medical treatments with complementary and alternative therapies, in order to provide comprehensive, patient-centered care.
Integrative medicine recognizes that health and wellness are influenced by a variety of factors, including physical, emotional, and spiritual health, and seeks to address the whole person, rather than just the symptoms of a disease or illness.
Integrative medicine may include a range of practices and therapies, such as acupuncture, chiropractic, herbal medicine, massage therapy, meditation, nutrition counseling, and other forms of traditional medicine.
Integrative medicine practitioners work with their patients to develop personalized treatment plans that take into account their unique needs and circumstances, and may incorporate a range of interventions to support healing and promote optimal health.
Integrative medicine is often used to complement conventional medical treatment, and may be recommended by healthcare providers to enhance the effectiveness of treatment or to alleviate side effects of conventional medical treatment.
While many integrative medicine practices have been shown to have some benefits, they may not be supported by scientific evidence or may not have undergone rigorous testing to determine their safety and efficacy. It is important to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider before using any integrative medicine practices or therapies, to ensure safe and effective treatment.
It is also important to note that some integrative medicine practices may have risks or side effects, and may interact with other medications or treatments. It is recommended to approach integrative medicine with an open mind, but also with a critical eye, and to use caution and common sense when considering any form of treatment.

![]()
Functional medicine Detailed descriptions
Functional medicine is a patient-centered, systems-oriented approach to healthcare that focuses on addressing the root causes of disease and illness, rather than just treating symptoms.
Functional medicine practitioners consider the interconnectedness of the body’s systems, and seek to identify and address imbalances and dysfunctions that may be contributing to a patient’s health problems.
Functional medicine may include a range of interventions, such as nutrition counseling, lifestyle modification, stress reduction techniques, and targeted use of supplements or medications.
Functional medicine practitioners work with their patients to develop personalized treatment plans that take into account their unique needs and circumstances, and may incorporate a range of interventions to support healing and promote optimal health.
Functional medicine is often used to complement conventional medical treatment, and may be recommended by healthcare providers to enhance the effectiveness of treatment or to alleviate side effects of conventional medical treatment.
Functional medicine has been shown to be effective in addressing a range of health conditions, including chronic disease, autoimmune disorders, digestive disorders, hormonal imbalances, and other complex health issues.
It is important to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider before using any functional medicine practices or therapies, to ensure safe and effective treatment. It is also important to note that some functional medicine practices may have risks or side effects, and may interact with other medications or treatments. It is recommended to approach functional medicine with an open mind, but also with a critical eye, and to use caution and common sense when considering any form of treatment.

![]()
Palliative medicine Detailed descriptions
Palliative medicine, also known as palliative care, is a specialized medical approach that focuses on improving the quality of life of patients facing serious illnesses and their families. The goal of palliative medicine is to relieve pain, manage symptoms, and provide emotional, spiritual, and practical support for patients and their families.
Palliative medicine is often used in conjunction with other medical treatments, and may be recommended at any stage of an illness, from the time of diagnosis to the end of life. It is not limited to terminal illnesses, but can also be used to manage chronic illnesses or complex health conditions.
Palliative medicine practitioners work closely with their patients and families to develop personalized treatment plans that take into account their unique needs, values, and goals. Treatment plans may include a range of interventions, such as medication management, physical therapy, counseling, and spiritual care.
Palliative medicine can also help patients and their families navigate complex medical decisions, and can provide resources for addressing practical concerns, such as financial and legal issues.
Palliative medicine is not the same as hospice care, which is a form of palliative care that is provided at the end of life. While both palliative medicine and hospice care focus on improving quality of life and managing symptoms, palliative medicine can be provided at any stage of an illness, and is not limited to end-of-life care.
It is important to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider before using any palliative medicine practices or therapies, to ensure safe and effective treatment.

![]()
Sports medicine Detailed description
Sports medicine is a specialized branch of medicine that focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of injuries and illnesses related to sports and physical activity. Sports medicine practitioners work with athletes and other active individuals to help them prevent injuries, manage medical conditions, and recover from injuries.
Sports medicine may include a range of interventions, such as injury prevention, strength and conditioning programs, nutrition counseling, physical therapy, and targeted use of medication and other treatments.
Sports medicine practitioners often work in collaboration with other healthcare professionals, such as orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists, and athletic trainers, to provide comprehensive care to patients.
Sports medicine can be used to address a range of conditions, such as sprains and strains, concussions, fractures, and other injuries related to physical activity. It can also be used to manage medical conditions that may impact athletic performance, such as asthma, diabetes, and heart disease.
Sports medicine practitioners may work with athletes at all levels, from amateur to professional, and may provide care to individuals of all ages and abilities.
It is important to seek the guidance of a qualified sports medicine practitioner before engaging in physical activity or using any sports medicine practices or therapies, to ensure safe and effective treatment. It is also important to follow proper safety protocols and use appropriate protective gear to prevent injury during physical activity.

![]()
Occupational medicine Detailed descriptions
Occupational medicine is a specialized branch of medicine that focuses on the health and safety of workers in the workplace. Occupational medicine practitioners work with employers, employees, and regulatory agencies to promote safe working conditions and to prevent and manage work-related injuries and illnesses.
Occupational medicine may include a range of interventions, such as workplace hazard assessments, ergonomic evaluations, health and safety training, and targeted use of medication and other treatments.
Occupational medicine practitioners may also conduct medical evaluations of employees, to assess their fitness for work and to identify any underlying health conditions that may impact their ability to work safely and effectively.
Occupational medicine can be used to address a range of work-related health issues, such as occupational asthma, carpal tunnel syndrome, noise-induced hearing loss, and other conditions related to exposure to workplace hazards.
Occupational medicine practitioners may work in a variety of settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and private practices, and may provide care to individuals in a range of industries, such as manufacturing, construction, and healthcare.
It is important for employers and employees to work together to create a safe and healthy work environment, and to follow proper safety protocols and use appropriate protective gear to prevent injury and illness in the workplace. It is also important to seek the guidance of a qualified occupational medicine practitioner before engaging in work-related activities or using any occupational medicine practices or therapies, to ensure safe and effective treatment.

![]()
Preventive medicine Detailed descriptions
Preventive medicine is a branch of medicine that focuses on the prevention of disease and injury before they occur. Preventive medicine practitioners work to identify and mitigate risk factors, promote healthy lifestyles, and prevent the onset of disease or injury.
Preventive medicine may include a range of interventions, such as vaccinations, health screenings, counseling on healthy lifestyle behaviors, and targeted use of medication and other treatments.
Preventive medicine practitioners may also conduct research to identify patterns and risk factors for disease and injury, and may work with policymakers and public health officials to develop and implement public health interventions and policies.
Preventive medicine can be used to address a range of health issues, such as infectious diseases, chronic diseases, and injuries. It can also help to reduce healthcare costs by preventing the onset of disease and reducing the need for medical intervention.
Preventive medicine practitioners may work in a variety of settings, such as hospitals, clinics, public health agencies, and private practices, and may provide care to individuals of all ages and backgrounds.
It is important for individuals to take an active role in their own health and to engage in healthy lifestyle behaviors, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and regular health screenings. It is also important to seek the guidance of a qualified preventive medicine practitioner for individualized recommendations on disease prevention and healthy living.

![]()
Rehabilitation medicine Detailed descriptions
Rehabilitation medicine, also known as physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R), is a specialized branch of medicine that focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of physical impairments and disabilities resulting from injury or disease.
Rehabilitation medicine practitioners work with patients to restore function, improve mobility, and reduce pain and other symptoms. They may use a variety of interventions, such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and targeted use of medication and other treatments.
Rehabilitation medicine can be used to address a range of conditions, such as spinal cord injuries, stroke, traumatic brain injuries, amputations, and other injuries or illnesses that impact physical function and mobility.
Rehabilitation medicine practitioners may work in a variety of settings, such as hospitals, rehabilitation centers, and private practices, and may provide care to individuals of all ages and backgrounds.
It is important for patients to work closely with their rehabilitation medicine practitioner to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. Rehabilitation may involve a long-term commitment and may require ongoing therapy and support to achieve the best possible outcomes.

![]()
Longevity Medicine detailed descriptions
Longevity medicine, also known as anti-aging medicine, is a specialized branch of medicine that focuses on promoting healthy aging and extending the lifespan. Longevity medicine practitioners work to prevent and manage age-related disease and to optimize physical and cognitive function as individuals age.
Longevity medicine may include a range of interventions, such as lifestyle changes, nutritional counseling, hormone replacement therapy, supplementation, and targeted use of medication and other treatments.
Longevity medicine can be used to address a range of age-related health issues, such as cardiovascular disease, cognitive decline, osteoporosis, and other chronic diseases associated with aging.
Longevity medicine practitioners may work in a variety of settings, such as clinics and private practices, and may provide care to individuals of all ages and backgrounds.
It is important for individuals to take an active role in their own health and to engage in healthy lifestyle behaviors, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol use. It is also important to seek the guidance of a qualified longevity medicine practitioner for individualized recommendations on healthy aging and disease prevention. However, it is important to note that some of the practices within longevity medicine are controversial and may not have strong scientific evidence to support their effectiveness, so it is important to discuss any potential treatments with a qualified healthcare provider