We’ve probably been underestimating the role of inflammation in aging.
I think scientists and specially gerontologists are well aware of the role of inflammation in aging and chronic diseases, but under appreciated is the importance and the role of immunology.
Immunology is highly complicated form of biology. It is shocking that inflammation is not the original hallmark of aging but it is when it goes haywire and chronic.
Recent studies shows that if you induce aging in the immune system you can induce secondary aging in all organs.
Thymus is the organ have enormous implication on our abilities to maintain a proper immune responses, and thymus disappear before you are fifty.
We need to work a lot in this field to understand aging and improving Health span.
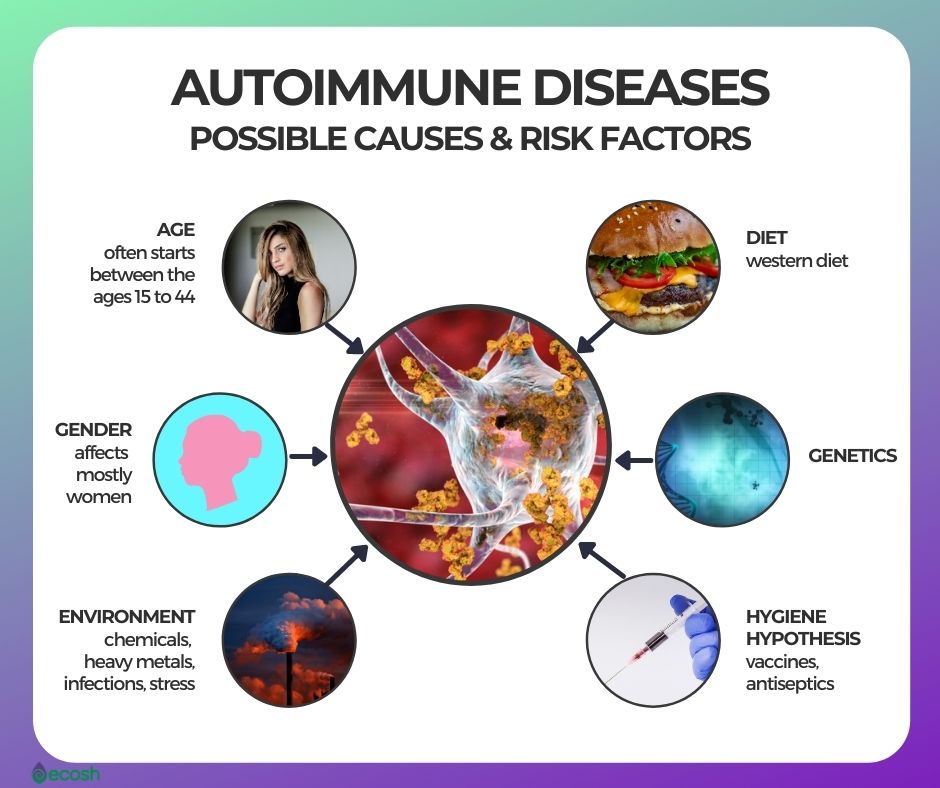
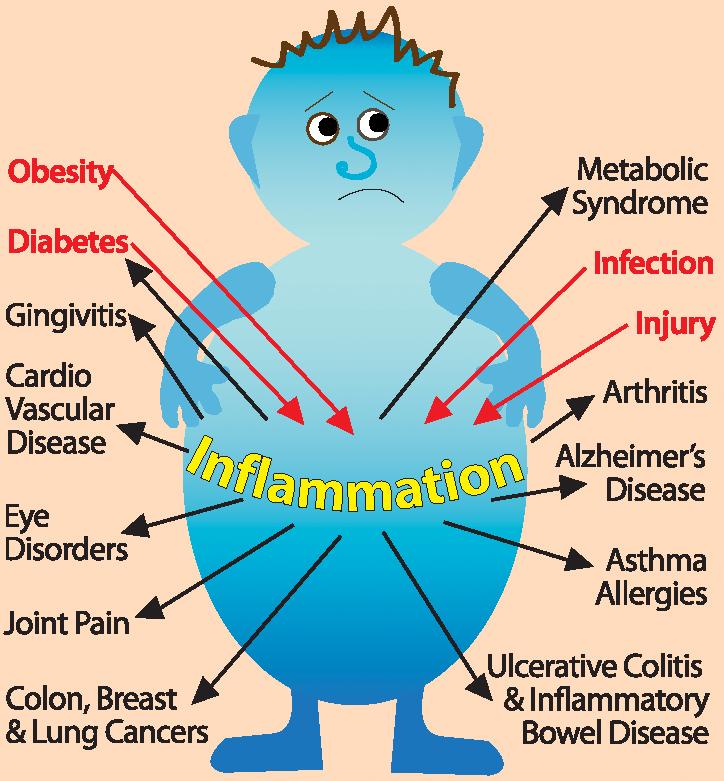
Inflammation is a normal physiological response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation has been linked to a variety of age-related diseases, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. Recent research suggests that chronic inflammation may play a major role in the aging process, and that targeting inflammation may be a potential strategy for preventing or delaying age-related diseases. However, more research is needed to fully understand the link between inflammation and aging.
What is the role of immune system in inflammation?
The immune system plays a crucial role in the inflammatory response. Inflammation is the body’s way of responding to injury or infection, and the immune system is responsible for recognizing and responding to harmful stimuli.
When the body detects a threat, the immune system releases a variety of molecules and cells, including white blood cells, to the affected area. These molecules and cells help to fight off the invader, remove damaged cells, and repair tissue. They also cause the blood vessels to dilate and become more permeable, which allows more immune cells and other molecules to reach the affected area. This causes inflammation and redness, heat, swelling and pain in the affected area.
The immune system is also responsible for regulating the inflammatory response. Once the threat has been eliminated, the immune system signals for the inflammatory response to stop. If the immune system is not functioning properly, it can lead to chronic inflammation, which can contribute to the development of various diseases and aging.
In short, the immune system plays a key role in the initiation and resolution of inflammation, and it is critical in maintaining the balance between a beneficial inflammatory response and a harmful one.
What is the role of diet in inflammation and chronic diseases?
[Currently, I think, the whole concept of pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory diets rather belongs to the realm of health podcasts than it is being studied hardcore in the laboratory. Yes, there are some foods, such as those high in saturated fats, that are pro-inflammatory. But when I’m reading articles about this or that anti-inflammatory diet, my question is always, what’s the evidence for this? And when you start looking into it, it’s not that much.]
Erick Verdin said in recent interview
Diet can play a significant role in both inflammation and the development of chronic diseases. Certain foods and nutrients have been shown to promote inflammation, while others can help to reduce it.
A diet high in processed foods, saturated fats, and added sugars can promote inflammation in the body. These foods can cause an increase in the production of inflammatory molecules, such as cytokines and eicosanoids. In contrast, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help to reduce inflammation. These foods are high in antioxidants, phytochemicals, and other anti-inflammatory compounds.
A diet high in omega-6 fatty acids and low in omega-3 fatty acids can also promote inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties, while omega-6 fatty acids can promote inflammation. A diet that emphasizes foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, can help to reduce inflammation. <click the link
Diet also plays a role in the development of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and added sugars can increase the risk of these diseases, while a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to reduce the risk.
Diet also plays a role in the development of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and added sugars can increase the risk of these diseases, while a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to reduce the risk.
Overall, diet plays a key role in regulating inflammation and the development of chronic diseases. Following a diet that emphasizes whole, nutrient-dense foods, and reducing processed foods and added sugars can help to reduce inflammation and lower the risk of chronic disease.
What Are The Pro And Con Of Keto Diet?
The ketogenic diet, or “keto” diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that aims to induce a state of ketosis, in which the body burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. This diet has been used as a treatment for certain medical conditions, such as epilepsy, and has also been popularized as a weight loss and performance-enhancing diet.
Pros of the keto diet include:
1-Weight loss: The keto diet can lead to significant weight loss, as it causes the body to burn fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. This can lead to a reduction in body fat and an improvement in body composition.
2-Improved blood sugar control: By reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat intake, the keto diet can help to improve blood sugar control in people with diabetes.
3-Reduced seizures: The keto diet has been used as a treatment for seizures in people with epilepsy, and it has been shown to be effective in reducing seizures in some people.
Cons of the keto diet include:
1-Difficulty sticking to the diet: The keto diet can be difficult to stick to, as it requires a significant reduction in carbohydrate intake and an increase in fat intake. This can be challenging for some people, and may not be sustainable long-term.
2-Nutrient deficiencies: The keto diet can lead to deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as fiber and certain vitamins and minerals, as it emphasizes high-fat foods and restricts certain food groups, such as fruits and whole grains.
3-Increased risk of heart disease: The high-fat intake on the keto diet may increase the risk of heart disease by elevating cholesterol levels and increasing the risk of other cardiovascular diseases.
It’s important to note that the ketogenic diet isn’t for everyone and it’s not recommended for long-term use without medical supervision. It’s always best to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any new diet, especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions or taking any medications.

Does it raise LDL level in blood and that may be alarming?
The ketogenic diet can lead to an increase in LDL cholesterol levels, also known as “bad” cholesterol. This is because the diet is high in fat, and some of the fats that are consumed on the diet are saturated fats, which can increase LDL cholesterol levels.
However, it’s important to note that not all LDL cholesterol is created equal. LDL particles come in different sizes, and the pattern of LDL particles can be more or less dangerous for cardiovascular health. A diet that increases the number of small dense LDL particles is considered more harmful than a diet that increases the number of large LDL particles. The ketogenic diet may lead to an increase in the number of small LDL particles, which is considered a risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Additionally, the ketogenic diet can also lead to an increase in HDL cholesterol, which is considered “good” cholesterol, and this can have a beneficial effect on cardiovascular health.
It’s important to note that everyone’s response to the diet is different and some people may experience a significant increase in LDL cholesterol while others may not. That’s why it’s important to have regular check-up with a healthcare provider and have your cholesterol levels monitored while on the diet.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional and have your cholesterol levels monitored before and during a ketogenic diet, especially if you have a history of high cholesterol or cardiovascular disease. This can help you to make informed decisions about whether or not the diet is appropriate for you, and whether any adjustments to the diet or medication regimen are necessary.

Fruits are delicious and loaded with phytonutrients but also high in sugar
Fruits are a great source of vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients, which are naturally occurring compounds found in plants that have health-promoting properties. They are also a good source of dietary fiber and water, which can help to promote feelings of fullness and hydration. However, fruits do contain natural sugars, which can be a concern for some people, particularly for those with diabetes or other conditions that affect blood sugar levels.
It’s true that fruits contain natural sugars, such as fructose, but it’s important to note that these sugars are packaged with other important nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and dietary fiber that can help to slow down the absorption of sugar in the body. Also, most fruits are low in calories, and they are often considered “low glycemic index” foods, which means that they don’t cause rapid spikes in blood sugar.
It’s recommended to include fruits as part of a healthy and balanced diet. However, if you are trying to manage your blood sugar levels, it’s important to choose fruits that are lower in sugar, such as berries, citrus fruits, and apples. You can also control portion sizes, and consume fruits in moderation.
Additionally, it’s important to note that not all sugars are created equal. Natural sugars found in fruits have a different metabolic impact than added sugars found in processed foods. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugars intake to no more than six teaspoons (24 grams) for women and nine teaspoons (36 grams) for men daily.
Overall, fruits are a nutritious and delicious food that can be enjoyed as part of a healthy diet, but it’s important to be mindful of portion sizes and to choose lower-sugar options, especially if you are trying to manage your blood sugar levels.
What about exercising during that 16-hour window when you’re on intermittent fasting?
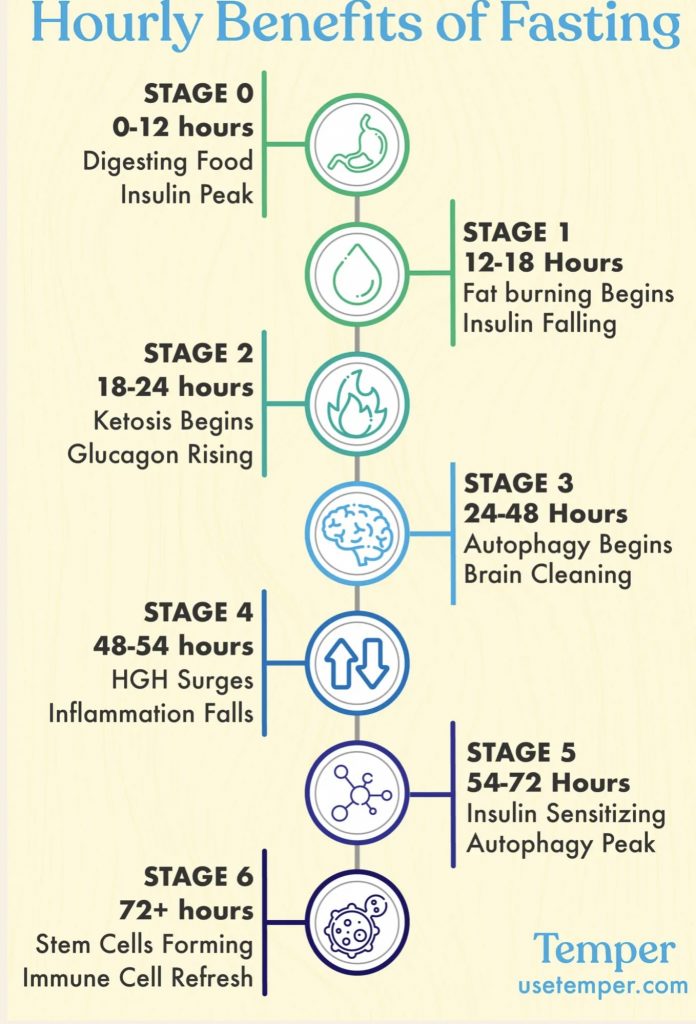
Exercising while participating in intermittent fasting can be a bit more challenging than exercising at other times, as the body may not have the same energy levels or glucose availability as it would have during a feeding window.
However, many people find that they are able to exercise effectively while participating in intermittent fasting, as long as they pay close attention to their body’s signals and make adjustments as needed.
During the fasting period, the body is in a state of ketosis, which means it is burning fat for energy. This can be beneficial for endurance exercise but may not be as effective for high-intensity or strength training. Low-intensity exercise such as yoga, or walking may be more suitable during the fasting period.
It’s important to listen to your body and adjust the intensity and duration of your workout as needed. If you feel weak or lightheaded during a workout, it may be a sign that your body needs more fuel, and it’s best to stop or reduce the intensity of your workout.
It’s also important to be well hydrated during the fasting period, as dehydration can make it more difficult to exercise. It’s also a good idea to schedule your workout during the latter half of your fasting window, when the body has had a chance to adjust to the fasted state.
It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise routine, especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions or are new to exercise.

Rejuvenation and longevity are the buzz words, but it look like rich people will be the most beneficial
Rejuvenation and longevity are areas of research that are gaining increasing attention, and many scientists and companies are working on developing technologies and treatments that can help to extend human lifespan and improve overall health in later life. However, as with many new technologies, there is a concern that the benefits of these treatments may not be equally distributed.
It is true that some of the first treatments and therapies to emerge from this research may be expensive, and may only be accessible to people who can afford to pay for them. This could lead to a situation where the benefits of rejuvenation and longevity treatments are concentrated among the wealthy, while others do not have access to them.
However, it’s important to note that many of the research in this field is still in its early stages, and it is unclear how much these treatments will cost in the long run. It is also possible that over time, as the technology and treatments improve, the costs will decrease and become more accessible to a wider range of people.
Additionally, governments and non-profit organizations are also investing in this field, and they may find ways to make these treatments affordable for the general public.
It’s also important to consider that longevity and rejuvenation are not only about extending human lifespan, but also about improving the quality of life and reducing the burden of diseases in older adults. By improving the health of older adults, the society will benefit from a more productive and active population.
Overall, it’s important to keep in mind that the field of rejuvenation and longevity is rapidly evolving, and it’s too early to predict exactly how these treatments will be made available to the public. It is important for society to have a conversation about equitable access to new treatments and technologies, so that the benefits can be shared by all.
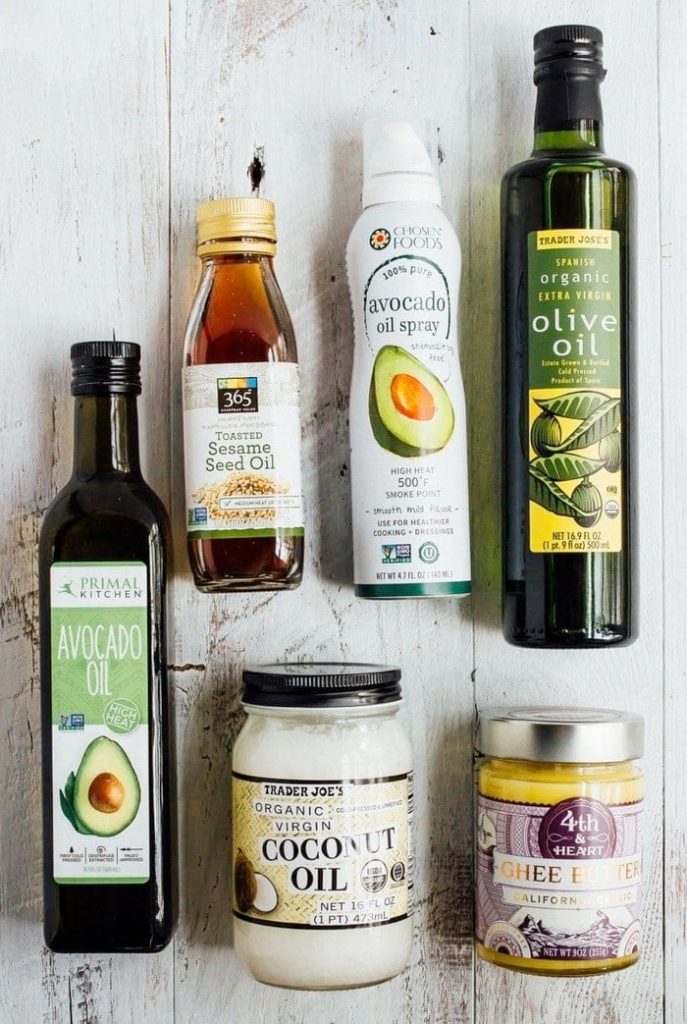

What are the best cooking oil we should use for healthy living
When choosing a cooking oil, it’s important to consider the oil’s smoke point and its fatty acid composition.
Smoke point is the temperature at which an oil begins to smoke and break down, releasing harmful compounds. Oils with high smoke points, such as avocado oil, coconut oil, and grapeseed oil, are good choices for high-heat cooking methods like stir-frying and sautéing.
The fatty acid composition of an oil is also important to consider. Unsaturated fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are considered to be healthier for the heart compared to saturated fats. Oils that are high in monounsaturated fats such as olive oil, avocado oil, and canola oil are good choices for heart health.
Here are some of the best cooking oils for healthy living:
• Extra-virgin olive oil: This oil is high in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants. It’s great for dressings, marinades, and low-heat cooking methods like sautéing and baking.
• Avocado oil: This oil is high in monounsaturated fats and has a high smoke point, making it great for high-heat cooking methods like stir-frying and deep-frying.
• Canola oil: This oil is high in monounsaturated fats and low in saturated fats. It has a neutral flavor and a high smoke point, making it a versatile oil for cooking.
• Coconut oil: This oil is high in saturated fats and has a high smoke point, making it good for high-heat cooking methods like stir-frying and sautéing.
• Flaxseed oil: This oil is high in polyunsaturated fats, including omega-3 fatty acids, and should be used only for low-heat cooking methods or dressings, as it is sensitive to heat and light.
It’s important to remember that no one cooking oil is the best for everyone. It’s always good to have a variety of oils in your pantry, and use them depending on the recipe and cooking method.
Break down the amount of protein, lipids and carbohydrate, the balance daily consumption
The recommended daily macronutrient intake for an adult varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and activity level. In general, a healthy diet should include a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids (fats).
Proteins :
The daily recommended intake for protein is 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight. This means that a sedentary adult needs around 56 grams of protein per day. However, for people who are physically active or looking to build muscle, a higher protein intake may be beneficial.
Carbohydrates:
The recommended daily intake of carbohydrates is 130 grams per day, which is about 45-65% of total daily calorie intake. Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy, and they should come from whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
Lipids (Fats):
The recommended daily intake of fats is 20-35% of total daily calorie intake. It is important to choose healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, found in foods like nuts, seeds, avocado, and fatty fish.
It’s worth noting that these recommendations are general and that it’s always best to consult with a doctor or a registered dietitian to determine the best macronutrient balance for you, depending on your personal health history, goals, and lifestyle.
It’s also important to remember that nutrient needs also change depending on the stage of life and the health status, pregnant women, lactating women, elderly people, and people with specific health conditions may have different requirements.

the above mentioned diet plan Is good in old age over 60?
As people age, their nutritional needs may change. It is important for older adults to pay attention to their nutrient intake in order to maintain good health.
Protein:
As people age, their muscle mass may decline, which is why it is important for older adults to consume enough protein to help maintain muscle mass and strength. The recommended daily protein intake for older adults is around 1.0-1.2 grams per kilogram of body weight.
Carbohydrates:
Carbohydrates are still an important source of energy for older adults. However, older adults may need to pay more attention to the quality of carbohydrates they consume, such as choosing whole grains over refined carbohydrates.
Lipids (Fats):
Older adults may need to pay more attention to their fat intake in order to maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. It is important for older adults to choose healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, and to limit their intake of saturated and trans fats.
It’s also important for older adults to consume enough vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin D and calcium, to support bone health. Additionally, older adults may need to consume more fluids than younger adults to stay hydrated.
It’s important to note that older adults have different health needs, and it’s always best to consult with a doctor or a registered dietitian to determine the best dietary plan for you, depending on your personal health history, goals, and lifestyle.

What about the exercise, type, timing and duration
Exercise is important for maintaining overall health and wellness, especially as people age. Regular physical activity can help prevent chronic diseases, improve cardiovascular health, maintain muscle mass and strength, and improve balance and flexibility.
Types of Exercise:
For older adults, a combination of aerobic exercise, resistance training, and flexibility exercises are recommended. Aerobic exercise, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, can improve cardiovascular health and increase endurance. Resistance training, such as weight lifting or bodyweight exercises, can help maintain muscle mass and strength. Flexibility exercises, such as yoga or stretching, can help improve range of motion and reduce the risk of falls.
Timing of Exercise:
The best time to exercise is a personal preference, but it’s important to make sure that you are consistent and make it a part of your daily routine. It’s also important to consider any medications or medical conditions that may affect your exercise schedule.
Duration of Exercise:
The American College of Sports Medicine recommends that older adults engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, in addition to muscle-strengthening activities at least two days per week. However, older adults who are new to exercise should start with shorter duration and lower intensity, and gradually increase as their fitness level improves.
It’s important to note that before starting any exercise program, older adults should consult with their healthcare provider to ensure that it is safe for them to do so. This is especially important for older adults who have chronic health conditions or limited mobility.
Loneliness is more dangerous than obesity

Loneliness and social isolation have been linked to a number of negative health outcomes, including an increased risk for chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and depression. Studies have also found that lonely individuals have a higher risk of premature death compared to those who are not lonely.
On the other hand, Obesity is a major public health concern and has been linked to a number of chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. People who are obese are at a higher risk of premature death compared to those of a healthy weight.
Both Loneliness and Obesity can have significant negative impact on people’s health and well-being. Studies suggest that people who are lonely and/or have a high body mass index (BMI) have a greater risk of premature death than people who are not lonely and have a healthy BMI.
It’s important to understand that both loneliness and obesity are complex issues that can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Interventions to address loneliness and obesity may include social support, therapy, and lifestyle changes such as regular physical activity and a healthy diet.
It’s important for individuals to be aware of their social connections, to make an effort to build and maintain healthy relationships, and to seek support when needed. And also to be mindful of their weight and overall health, and to make changes to their lifestyle to improve it.
In future is longevity medicine is going to replace the conventional medicine?
We need to understand that what marvels conventional medicine played in human wellness.
Contemporary medicine is disease control system and highly successful in controlling disease, infectious disease have been controlled by vaccination, surgery is a big win in medicine and nobody can deny the role of antibiotic in human health.
But as for chronic diseases it is not that successful because it philosophy is based on symptoms, it is symptomatic and addresses disease like whack a mole game, it doesn’t work on rote cause of the disease. You start with one pill and end up with a bulk, you live longer but miserable life with chronic suffering that is not win win game.
Longevity medicine’s philosophy is addressing the root cause of the disease not the symptom,it is a slow process and preventive and holistic, and should be implemented as soon as possible.
In future both system will argument each other and synergetic effect will be substantial. Unfortunately if disease is already developed, mean urgently need to address it first and then intervening longevity medicine.
There are all alternative medicine out there human have been using since eons, like herbal, Ayurvedic, Chinese herbal medicine, acupuncture,Homeopathy, psychedelic and meditation,
etc you name it.