03:11
Depression: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment Options
Mental health issues are ubiquitous and other disorders, like metabolic syndrome, cancer, cardio vascular disease, brain stroke, autoimmune disease etc, you name it. What are the underlying causes?
There are many different factors that can contribute to the development of health issues. Some of the most common causes include:
1- Genetics: Some health conditions are caused by genetic mutations passed down from parents to children. For example, certain cancers and genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia are caused by specific genetic mutations.
2- Lifestyle: Factors such as diet, exercise, and smoking can contribute to the development of certain health conditions. For example, a diet high in saturated fat and sugar can increase the risk of heart disease, while a diet high in fruits and vegetables can reduce the risk. Similarly, smoking is a major risk factor for lung cancer and other health issues.
3- Environmental Exposure: Exposure to toxins and pollutants in the environment can also contribute to the development of health issues. For example, exposure to asbestos can increase the risk of lung cancer, while exposure to pesticides can increase the risk of neurological disorders.
4- Aging: As we age, our bodies are more susceptible to certain health conditions, such as heart disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
5- Microorganisms: Certain health conditions are caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Examples include infections such as tuberculosis and malaria, and chronic conditions like periodontitis and Crohn’s disease.
6- Trauma: Trauma such as physical, emotional or psychological can also lead to health issues such as PTSD, anxiety and depression.

It’s worth noting that many health conditions are caused by a combination of these factors, and that the specific causes of a particular condition can vary from person to person. Additionally, some health issues are multifactorial in nature, meaning they are caused by a combination of several different factors.
What are the latest and widely accepted theories of depression?
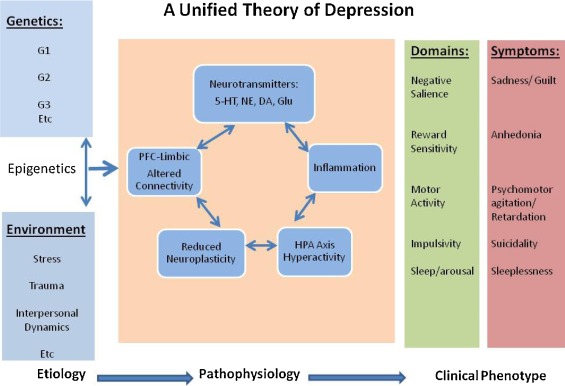
There are several theories of depression that are currently accepted in the scientific community. One of the most widely accepted is the monoamine hypothesis, which suggests that depression is caused by a deficiency of certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, in the brain. Another theory is the cognitive theory of depression, which suggests that negative thoughts and beliefs can lead to the development and maintenance of depression. The diathesis-stress model, which suggests that depression is caused by the interaction of genetic vulnerability and environmental stressors. Additionally, there is growing evidence for the role of inflammation in depression, with research suggesting that chronic low-grade inflammation may contribute to the development of depression.
![]()
It might be the case that depression is an umbrella term, different underlying causes and different types of depression
Yes, that is correct. Depression is a complex disorder that can have multiple causes and can manifest in different ways. The symptoms of depression can vary widely from person to person, and the causes of depression are likely to be different for different individuals. Some people may experience depression as a result of a traumatic event or a significant loss, while others may have a genetic predisposition to depression. Additionally, some people may experience depression as a result of a medical condition or as a side effect of certain medications.
There are different types of depression that have different characteristics, such as major depressive disorder, persistent depressive disorder, and seasonal affective disorder. Major depressive disorder (MDD) is the most common type of depression, characterized by a persistent feeling of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities. Persistent depressive disorder (PDD) is characterized by a depressed mood that lasts for at least 2 years. Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that occurs in the fall and winter months, when there is less natural sunlight.
Given that depression is a complex disorder, it is important to receive an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan from a qualified healthcare professional.
![]()
What treatment options are that work the best to alleviate the symptoms, and how it is diagnosed to find out what type of depression is?

The most effective treatment for depression varies from person to person, as the causes and symptoms of depression can differ greatly. However, there are several treatment options that have been shown to be effective in treating depression. These include:
1- Medication: Antidepressant medication, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can be effective in treating depression by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain.
2- Therapy: Talk therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy (IPT), can help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to their depression.
3- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT): ECT is a medical procedure in which electrical currents are passed through the brain to induce a seizure. ECT is usually used when other treatments have not been effective.
4- Light therapy: For seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
5- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, good sleep hygiene, stress management techniques, and healthy eating habits can help alleviate symptoms of depression.
6- Meditation and yoga

Meditation and yoga have been shown in some studies to have a positive effect on reducing symptoms of depression. They can help to reduce stress and anxiety, improve mood, and increase feelings of well-being. However, it is important to note that these practices should not be used as a replacement for professional medical treatment. If you are experiencing depression, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for you

To diagnose depression, a healthcare professional will typically conduct a physical examination, a psychological evaluation, and a diagnostic interview. The healthcare professional will also ask about the symptoms, including how long they have been present, how severe they are, and how they affect the person’s ability to function. The professional may also use a standardized questionnaire or depression scale, such as the Beck Depression Inventory or the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression, to help make a diagnosis.
In addition, some recent research suggests that biomarkers such as inflammation, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and cortisol, may be useful in identifying the subtypes of depression.
It’s important to note that there is no single test to definitively diagnose depression and it’s a process that involves multiple steps and assessment to identify the type of depression and to provide the appropriate treatment.
![]()

What is the Beck Depression Inventory or the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression diagnostic
The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) and the
Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD) are both commonly used self-report scales to assess the severity of depression.
The BDI is a 21-item questionnaire that assesses the symptoms of depression, such as feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities. Each item is rated on a scale of 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe symptoms of depression. The BDI is widely used in research and clinical settings, as it is relatively easy to administer and score.
The HRSD is a 17-item questionnaire that assesses the symptoms of depression, such as feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities. Each item is rated on a scale of 0 to 4, with higher scores indicating more severe symptoms of depression. The HRSD is widely used in research and clinical settings, as it is considered to be a reliable and valid measure of depression.
Both the BDI and the HRSD are widely used and accepted as a diagnostic tool for depression, but it is important to note that they are not diagnostic tools on their own. They are used as part of a comprehensive assessment, in conjunction with a clinical interview and examination. They should be used in combination with other information, such as a patient’s medical history and psychiatric history, to make a diagnosis of depression.
![]()
WebMD Site for depression click here >blood test Currently, there is no specific blood test that can diagnose depression, but there test helpful for depression diagnosis. While some researchers have investigated the possibility of using biomarkers such as inflammation, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), or cortisol levels as a diagnostic tool for depression, these tests are not yet widely used in clinical practice. While these biomarkers might be useful to identify subtypes of depression and to monitor treatment response, they are not yet specific or sensitive enough to be used as a standalone diagnostic tool.
The diagnosis of depression is typically made based on a combination of factors, including a patient’s symptoms, medical history, and psychiatric history. It is generally done through a clinical interview and examination, along with self-report scales such as the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) or the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD) to assess the severity of depression symptoms.
It’s important to note that while there is no blood test to diagnose depression, blood tests may be used to rule out other possible causes of symptoms, such as thyroid problems or anemia.
![]()
Hormonal imbalances may be one of the cause Hormonal imbalances can be a potential cause of depression.
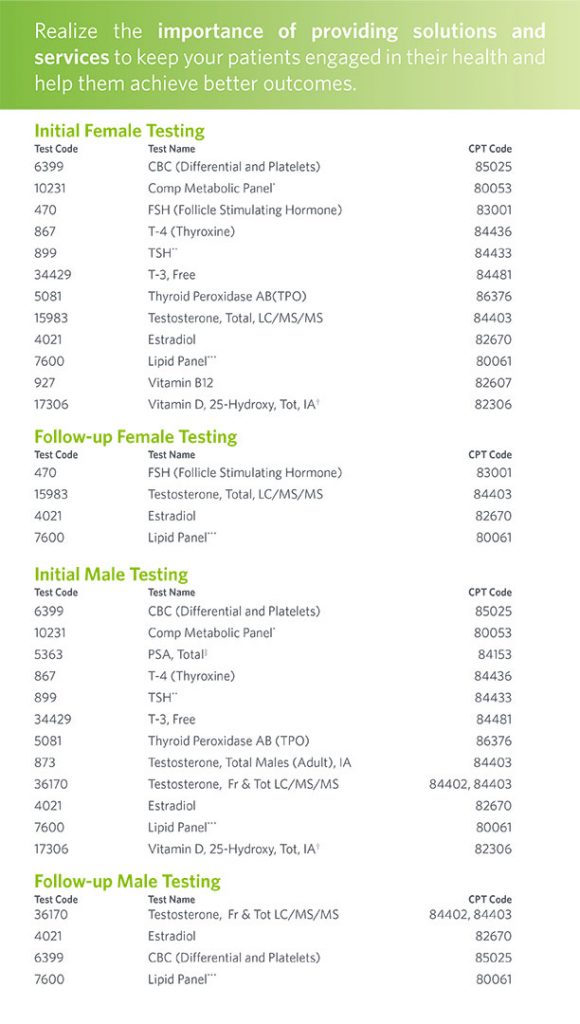
Hormones play a critical role in regulating mood, and imbalances in certain hormones can lead to symptoms of depression. Some of the hormones that have been associated with depression include:
1- Serotonin: This neurotransmitter is involved in regulating mood, sleep, and appetite. Low levels of serotonin have been linked to depression.
2- Norepinephrine: This neurotransmitter is involved in regulating mood, attention, and stress response. Low levels of norepinephrine have been linked to depression.
3- Cortisol: This hormone is released by the adrenal glands in response to stress. High levels of cortisol have been linked to depression.
4- Thyroid hormones: Thyroid hormones play a role in regulating metabolism and energy levels. Imbalances in thyroid hormones can lead to depression.
5- Melatonin: This hormone is involved in regulating sleep. Low levels of melatonin have been linked to insomnia and depression.
6- Testosterone: Low levels of testosterone in men have been linked to depression.
It’s important to note that hormonal imbalances are not the only cause of depression, and many other factors such as genetics, stress, trauma, and life events also play a role. If a person suspects a hormonal imbalance is contributing to their depression, they should talk to a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and treatment.
It is also important to note that a blood test can be done to check the hormonal levels, but it’s not a definitive test to diagnose depression, it should be combined with other assessment methodologies.
![]()
Are some alternative therapies work well, like herbal or magnetic Tran cranial induction therapy There are a variety of alternative therapies that have been proposed as treatments for depression, such as herbal remedies, magnetic cranial induction therapy, and others. However, the effectiveness of these therapies for treating depression is not well established and more research is needed.
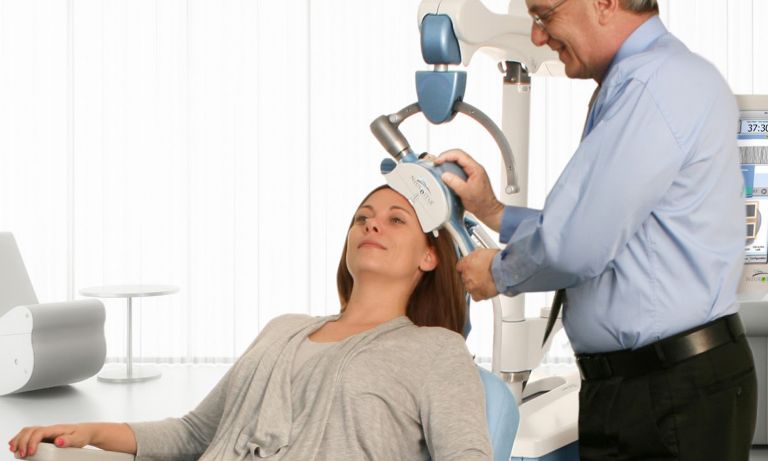
Herbal remedies: Some herbs, such as St. John’s wort, have been studied as potential treatments for mild to moderate depression. However, the results of these studies have been mixed and more research is needed to determine the effectiveness of these herbs for treating depression. Additionally, some herbs can interact with other medications, so it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before using any herbal remedies.
Magnetic cranial induction therapy: This therapy involves the use of a magnetic field to stimulate the brain. Some studies have suggested that this therapy may be effective for treating depression, but more research is needed to confirm these findings.
It’s important to note that alternative therapies should not be used as a substitute for established treatments for depression, such as therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. People who are considering alternative therapies should talk to a healthcare professional first.


It is important to understand that depression is a serious condition and requires proper diagnosis, treatment and care. Alternative therapies may have some benefits, but they are not a substitute for established treatments, which have been shown to be effective through scientific research. It’s important to work with a mental health professional when seeking treatment for depression.
![]()
What are the herbs used for treatments Herbs have been used for centuries to treat a variety of health conditions, including depression. Some of the most commonly used herbs for treating depression include:
1- St. John’s Wort: This herb has been widely studied for its potential to treat mild to moderate depression. It is believed to work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin.
2- Saffron: Some studies have suggested that this herb may be effective for treating mild to moderate depression. Saffron has been found to have an effect on the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin, which are thought to play a role in regulating mood.
3- Rhodiola rosea: This herb is traditionally used to improve mood, reduce stress and fatigue, and enhance cognitive function. Some studies suggest that Rhodiola rosea may be beneficial for people with mild to moderate depression.
4- Ginkgo biloba: This herb is believed to increase blood flow to the brain, which may help with depression symptoms. Some studies have suggested that Ginkgo biloba may be effective for treating mild to moderate depression.
5- Valerian root: This herb is often used as a natural remedy for insomnia and anxiety. Some studies suggest that valerian root may have a mild anti-anxiety effect, which may be beneficial for people with depression.
6- Ashwagandha: This herb has been traditionally used for anxiety and stress. Some studies have suggested that ashwagandha may be effective for treating mild to moderate depression.
It’s important to keep in mind that the safety and effectiveness of these herbs for treating depression have not been established. Many herbs can interact with other medications or have other side effects. Consultation with a healthcare professional is important before using any herbal remedy.

![]()
Latest guidelines for psychiatric treatment The latest guidelines for psychiatric treatment vary depending on the specific condition being treated. However, in general, current guidelines for the treatment of psychiatric disorders emphasize a combination of different approaches, including therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
1- Therapy: Various forms of therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, interpersonal therapy, and psychodynamic therapy, are widely used to treat psychiatric disorders.
2- Medication: Antidepressants, antipsychotics, and mood stabilizers are commonly prescribed to treat a variety of psychiatric conditions, including depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder.
3- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, healthy diet, and getting enough sleep can help to improve symptoms of psychiatric disorders. Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness and meditation can also be beneficial.
4- Recovery-oriented practices: Recovery-oriented practice approach is widely accepted and implemented in psychiatric treatment, this approach is based on the person-centered and empowering practices, it helps people to set their own goals, and receive the support they need to achieve them.
5- Integrated care: Integrated care is becoming increasingly important in the treatment of psychiatric disorders. This approach involves coordinating care between different healthcare providers, such as primary care physicians, psychiatrists, and other specialists.
It’s important to note that the specific treatment plan will depend on the individual patient and their specific condition. It is important to work with a mental health professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that takes into account the patient’s unique needs and preferences.
Also, it’s important to note that guidelines are updated regularly as new research becomes available, so it’s a good idea to stay informed about the latest developments in psychiatric treatment.
![]()
Latest antidepressants available with the efficacy
There are several different types of antidepressants available, each with their own unique mechanism of action and side effect profile. Some of the newer or latest antidepressants include:
1- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): SSRIs are the most commonly prescribed antidepressants. They work by increasing the levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the brain. Examples of SSRIs include fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), and paroxetine (Paxil).
2- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): SNRIs also increase the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, but they target both serotonin and norepinephrine. Examples of SNRIs include venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta).
3- Atypical Antidepressants: These are a group of antidepressants that don’t fit into the traditional categories of SSRIs or SNRIs. They work differently than the traditional antidepressants. Examples include bupropion (Wellbutrin), trazodone (Desyrel) and mirtazapine (Remeron).
4- Norepinephrine-Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitors (NDRIs): These are a newer class of antidepressants that selectively target the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and dopamine. Examples include Bupropion (Wellbutrin) which is also an atypical antidepressant.
5- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) are older classes of antidepressants that are still used today, but less commonly because of their potential side effects.
It is important to note that the efficacy of antidepressants varies from person to person, and it is important to work with a mental health professional to determine the best treatment plan for an individual. Additionally, it’s also important to note that the FDA approval process and clinical trials may not include all populations, and the efficacy and safety of these medications may vary among different populations.
![]()
What are the Ayurvedic and Chinese Medicine (TCM) and remedies for depression?

Ayurvedic and Chinese medicine are traditional systems of medicine that have been used for thousands of years to treat a variety of health conditions, including mental health conditions such as depression.
In Ayurvedic medicine, depression is considered to be caused by an imbalance in the doshas, or the body’s natural energies. Treatment may include a combination of herbs, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications to restore balance to the doshas. Common herbs used in Ayurvedic medicine for depression include ashwagandha, Shankhpushpi, and Brahmi.
Chinese medicine, also known as Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), views depression as a imbalance in the body’s energy, called Qi (pronounced “chee”). Acupuncture, herbal medicine and dietary therapy are used to restore balance and improve mental health. Chinese herbal medicine commonly used for depression include Chinese skullcap, Chinese peony and Chinese licorice.
It’s important to note that while these traditional therapies may be helpful for some individuals, they should not be used as a replacement for conventional medical treatment and should be used under the guidance of a qualified practitioner. Additionally, there is limited scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of these therapies for treating depression, and more research is needed to fully understand their potential benefits and risks.

![]()
Ketamine or other psychedelic could be helpful and are being studied currently
Ketamine and other psychedelics are being studied as potential treatments for depression and other mental health conditions.
Ketamine is an anesthetic that has been found to have rapid and robust anti-depressant effects. It is thought to work by increasing the levels of a neurotransmitter called glutamate in the brain, which can lead to the growth of new connections between brain cells. Some studies have shown that ketamine can provide rapid relief for symptoms of depression and suicidal thoughts in patients who do not respond to traditional antidepressants. However, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term safety and efficacy of ketamine as a treatment for depression.
Psychedelics, such as psilocybin (found in “magic mushrooms”), LSD, and DMT, are also being studied for their potential therapeutic effects. These substances have been found to have anti-depressant and anti-anxiety effects, and have been shown to lead to increased neuroplasticity and neurogenesis in the brain. However, further research is needed to determine their long-term safety and efficacy as treatments for depression and other mental health conditions.
It is important to note that the use of ketamine and other psychedelics for treatment purposes is not currently FDA-approved, and should not be used outside of a clinical trial or research setting. More studies are needed to determine the safety and efficacy of these substances as treatments for depression and other mental health conditions.
![]()
Native American medicine might’ve some remedies?
Native American medicine is a traditional system of healing that has been used by indigenous peoples of North America for thousands of years. It encompasses a wide range of practices, including spiritual ceremonies, herbal medicine, and healing through the use of natural elements.
In Native American medicine, mental health conditions such as depression are often viewed as being caused by an imbalance in the body and mind, and treatment may include a combination of spiritual ceremonies, herbal medicine, and changes in lifestyle to restore balance. Ceremonies such as the sweat lodge, which is used for purification and healing, and the use of tobacco, which is used to connect with the spiritual world, are commonly used to treat mental health conditions.

Herbs commonly used in Native American medicine for mental health conditions include sage, sweetgrass, and cedar. These herbs are often used in combination with other natural elements such as crystals, feathers, and animal parts for healing.
It is important to note that while traditional Native American medicine may be helpful for some individuals, it should not be used as a replacement for conventional medical treatment and should be used under the guidance of a qualified practitioner. Additionally, there is limited scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of these therapies for treating depression, and more research is needed to fully understand their potential benefits and risks
03:11

